
前言
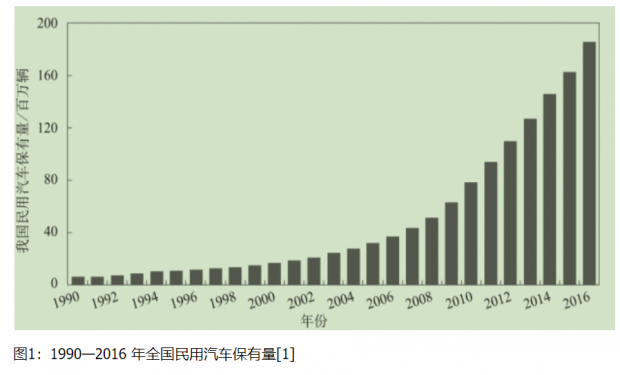
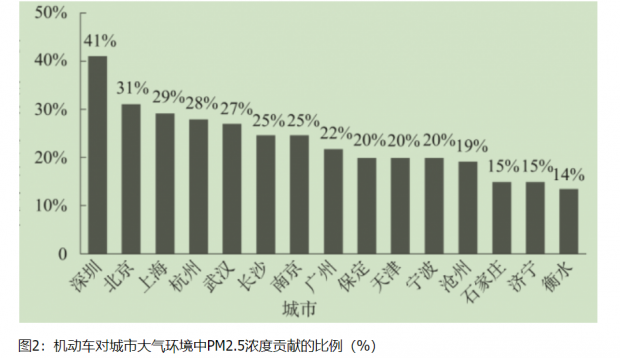
随着机动车保有量的快速增长,机动车污染物排放量居高不下,严重影响大气环境质量的持续改善,正在成为我国城市经济和社会发展中的一个重要环境问题,已引起相关部门和公众的极大关注和重视。交通污染特征及人群健康效应的研究对预防和减少大气污染物对公众身心健康的危害,具有十分重要的公共卫生学意义。
尾注:
[1]中国统计局.中国统计年鉴[M].北京:中国统计出版社,2017.
[2]李培,王新,柴发合,等.我国城市大气污染控制综合管理对策[J].环境与可持续发展,2011,36(5): 8-14
[3]Skrzypek M, Zejda J E, Kowalska M, et al.Effects of residential proximity to traffic on respiratory disorders in schoolchildren in upper Silesian Industrial Zone, Poland [J]. Int. J. Occup.Med.Environ. Health., 2013,26:83-91.
[4]Andersson M, Modig L, Hedman L, et al. Heavyvehicle traffic isrelated to wheeze among schoolchildren: a population-basedstudy in an area with low traffic flows [J]. Environ. Health.,2011,10:91.
[5]Gan W Q, Koehoorn M, Davies H W, et al.Long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and the risk of coronary heartdisease hospitalization and mortality [J]. Environ. Health. Perspect.,2011,119:501-507.
[6]Cooqan P F, White L F, Jerrett M, et al. Airpollution and incidence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus in black women livingin Los Angeles [J]. Circulation, 2012,125:767-772.
[7]Beckerman B S, Jerrett M, Finkelstein M, etal. The association between chronic exposure to traffic-related air pollutionand ischemic heart disease [J]. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health., 2012,75: 402-411.
[8]Wu S, Deng F, Huang J, et al. Blood pressurechanges and chemical constituents of particulate air pollution: Results fromthe healthy volunteer natural relocation (HVNR) study [J]. Environ. Health.Perspect., 2013,121:66-72.
[9]Wang S, Zhang J, Zeng X, et al. Associationof traffic-related air pollution with children’s neurobehavioral functions inQuanzhou, China [J]. Environ. Health. Perspect., 2009,117:1612-1618.
[10]de Kok T M, Driece H A, Hogervorst J G, etal. Toxicological assessment of ambient and traffic-related particulate matter:A review of recent studies [J]. Mutat. Res., 2006,613:103-122.
[11]XIE R, SABEL C E, LU X, et al. Long-termtrend and spatial pattern of PM 2.5 induced premature mortality in China[J].Environment international, 2016, 97: 180-186.
[12]吴潇萌.中国道路机动车空气污染物与 CO 2 排放协同控制策略研究 [D].北京:清华大学,2016.
[13]Wang X, Westerdahl D, Chen L C, et al.Evaluating the air quality impacts of the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games: On-roademission factors and black carbon profiles [J]. Atmos. Environ.,2009,43:4535-4543.
[14]Wu S, Deng F, Niu J, et al. Association ofheart rate variability in taxi drivers with marked changes of particulate airpollution in Beijing in 2008 [J]. Environ. Health. Perspect., 2010,118:87-91.
[15]Guo X R, Cheng S Y, Chen D, et al.Estimation of economic costs of particulate air pollution from road transportin China [J]. Atmos. Environ., 2010,44:3369-3377.
[16]Jia Y, Stone D, Wang W, et al. Estimatedreduction in cancer risk due to PAH exposures if source control measures duringthe 2008 Beijing Olympic were sustained [J]. Environ. Health. Perspect., 2011,119:815-820.
文章内容有删改,详情见《磐之石能源评论2019》





